Artificial intelligence (AI) will soon transform from a reactive tool into fully self-sufficient and autonomous AI agents that can perceive information and make decisions. It can then act without needing any direction or assistance from others. Once it is developed in a blockchain platform, these agents will be able to own wallets, conduct smart contracts, and interact with each other without a third-party supervisor.
The combination of adaptive AI decision-making with the trustless and transparent aspects of AI agents in blockchain creates a completely verifiable and self-sustaining digital economy. Each component of blockchain provides trustworthiness, secure foundations, and permissionless cooperation, while AI adds intelligent learning and strategic autonomy. Thus, users enjoy various possibilities on a platform that has decentralized AI agents who can bargain, trade, govern, and optimize real-time results.
This article will show how the transition of off-chain AI assistants to on-chain AI agents was designed, and also discuss the technical framework that supports the development of the two types of AI agents blockchain.
Understanding AI Agents in Blockchain Contexts
In the blockchain world, AI agents are programs that can read data, make decisions, and act on it directly on-chain or off-chain. Unlike bots, these autonomous AI agents have an identity that is fixed on the blockchain usually in the form of a wallet, and they own assets, sign transactions, and can be held accountable for what they do.
AI agents can operate by machine learning models, rules-based models, or a hybrid of both, but the blockchain provides the infrastructure for logging and enforcing what the agents do.
Blockchains have many benefits to ensure trustworthy operations of AI agents. Due to the immutability feature, a user’s actions, transactions, and decisions can be audited and tracked by anyone. The lack of a single point of authority means that an agent can operate in an open environment and not have to trust other parties.
Smart contracts enforce what an agent has agreed upon and help the agent perform its actions, make payments, and get the right results without the need for an intermediary.
The key aspects of the ecosystem include an agent’s on-chain identity, pay-per-result models, and interactions with other agents. The pay-per-result model compensates the agent for the result of its actions, rather than what it claims to have achieved. Interactions with other agents let them negotiate, coordinate, and compete with each other autonomously, creating a competitive environment.
Key Technologies Enabling Integration
The integration of AI agents with blockchain has been facilitated by a few important technologies, which we have discussed in the section below –
1. Verifiability
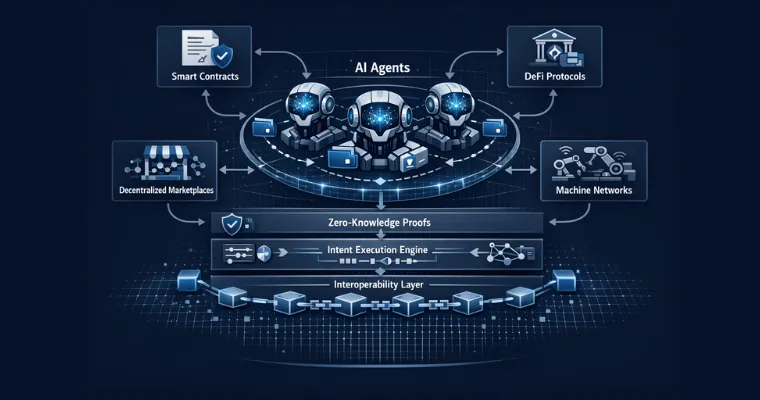
For individuals to trust autonomous on-chain economies on blockchain, it is important for verifiable AI agents to be able to verify that they acted as intended, within their constraints or defined rules, without compromising data or revealing any confidential information. In this way, Zero-Knowledge (ZK) proofs are used to prove that a given action took place while preserving both user privacy and agent accountability. To further ensure transparency of agent activity, on-chain audits record agent actions immutably, so that all network participants have an independent means of verifying agents’ behaviour and the outcomes of those behaviours. Through this, agents’ activity will always have an opportunity to be independently validated by participants across the entire blockchain community without requiring a central authority for oversight.
2. Intent Execution
By letting users express their higher-level objectives like maximum yields, intent execution removes much of the complexity of interacting with the blockchain. Intent-based AI agents can then convert these higher-level objectives into detailed process executions, involving many different steps across multiple protocols and blockchains. Interoperability technologies such as IBC allow secure communication and the exchange of digital assets between different chains, which enables agents to execute their intents across chains without interruption. This increase in usability, decrease in error rates, and ability of agents to change their execution paths dynamically based on real-world events improve the effectiveness and efficiency of agent activity.
3. Standards
Standards are vital for providing agents with a mechanism for scalable integration. ERC-8004 AI agents provide a secure way for agents to receive authority from institutions on the use of agents, which includes providing them with granular and revocable authorisation to perform tasks for them, for instance, to read, write, burn, destroy, or modify without revealing their private key. X402 for payments sets a standard method for transferring money, such as machine-to-machine payments, so that X402 protocol agents can pay for services to each other.
Real, Authentic Applications in Autonomous On-Chain Economies
- DeFi Automation: DeFi AI automation agents coordinate trading, liquidity, and yield management across blockchains, reacting in real-time to blockchain conditions. A project like SentientAGI has developed a protocol that allows this type of coordination between blockchains. It routes capital through multiple protocols to maximize returns while minimizing risk.
- Fraud Detection: Through real-time monitoring of smart contract transactions, AI agents in the machine economy blockchain can immediately flag exploitation, irregular patterns, or any form of exploitation, and take appropriate action. Partners like Ocean Protocol with AI blockchain integration with auditing can increase the security of smart contract transactions by continuously monitoring them.
- Decentralized Marketplaces: Decentralized marketplaces allow AI agents to autonomously interact with one another based on economic incentives, in terms of selling customer data or other services. Bittensor, for instance, provides a clear example of this model through its proof-of-intelligence system, allowing AI agents to compete to deliver high-quality outputs.
- Machine Economies in DePIN: Robots and physical devices have the ability to move money and engage in the machine economy blockchain without human intervention. In addition, ecosystems such as peaq with Fetch.ai enable machine-driven interactions to provide services without going through traditional intermediaries.
- Gaming and Virtual Worlds: AI agents have gained access to and the capability to manage items, trade goods, and evolve in a virtual economy. For example, Virtuals Protocol provides an agent token for AI agents in games that allows them to earn, own, transact, and thus persistently sustain virtual agents.
Challenges and Solutions
- Security: Autonomous AI agents that manage on-chain assets increase the attack surface. A few solutions for this issue are granular authorization, formal verification, sandboxed execution, and continuous on-chain monitoring.
- Scalability: AI blockchain integration can lead to a significant increase in transaction volumes. However, scalable designs are being developed that support layer-2 scaling, transaction batching, off-chain calculations, and efficient cross-chain communication.
- Compliance & Ethics: The issue of autonomous decision-making with blockchain AI convergence has created many questions regarding compliance and accountability. To ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards, the governance of AI agents should be completely transparent, the behaviour of agents verifiable, and the design of the agent to support regulatory awareness.
The AI blockchain integration is the basis for an agentic economy run by automated agents (AI) that can build, trade, and handle value on their own without the need for human involvement in each trade. The blockchain adds trust, clarity, and resolution, while AI adds decisions, efficiency, and execution. With the totality of the two, they offer more extensive on-chain-ledger economies.
With an increase in the use of blockchains, DeFi, machine networks, and virtual economies can effectively grow and develop. Over time, as regulatory concerns cloud the blockchain and a new set of security, scalability, and regulations arise, the agentic economy will evolve into an ongoing, continuous global commerce infrastructure for people and machines around the world.